Removing Heavy Metals From Power Plants Wastewater to Meet Government Regulations. is a process that can help power plants comply with regulations. Before the development of this technology, heavy metal waste was disposed of in rivers and lake bodies. Heavy metals are highly toxic, so they pose a serious risk to the ecosystem and millions of humans worldwide. In addition to being environmentally damaging, they also contribute to water pollution and a shortage of clean drinking water.
Depending on the location of your home, you might have to purchase an STP to handle your sewage. Generally, residential buildings need at least one STP to treat sewage. Many STPs are located underground, making them difficult to maintain. Moreover, you may not be able to inspect them without hiring an expert. It is better to consult a professional if you have any doubts about the process.
Challenges of heavy metal removal from power plant wastewater
Heavy metals are naturally occurring substances that can harm humans and the ecosystem. These pollutants occur at low concentrations, yet they can adversely affect human health and the environment. Heavy metals are extremely heavy and have a density of 5 g/cm3. They enter ecosystems through natural processes and anthropogenic activities. As a result, heavy metals are classified as major pollutants. In the United States, these pollutants include Al, Fe, Cr, Sb, As, Be, Cu, Pb, Hg, Ni, Se, Ag, and Zn.
EPA regulations for power plant wastewater and coal combustion residuals are forcing utilities to find solutions for heavy metals removal. The EPA regulations also require utilities to eliminate coal ash ponds and reduce the use of process water. Fortunately, there are solutions to this problem.
The problem of heavy metal pollution has become a hot topic of research and development. These contaminants persist in the environment for extended periods, and they cause harm to plants, animals, and humans. To address this problem, governments are using environmental regulations and monitoring studies to reduce the concentrations of heavy metals. Using non-toxic pesticides and renewable energy sources are also effective measures to reduce the amount of heavy metals in the environment.
Processes are used to remove heavy metals
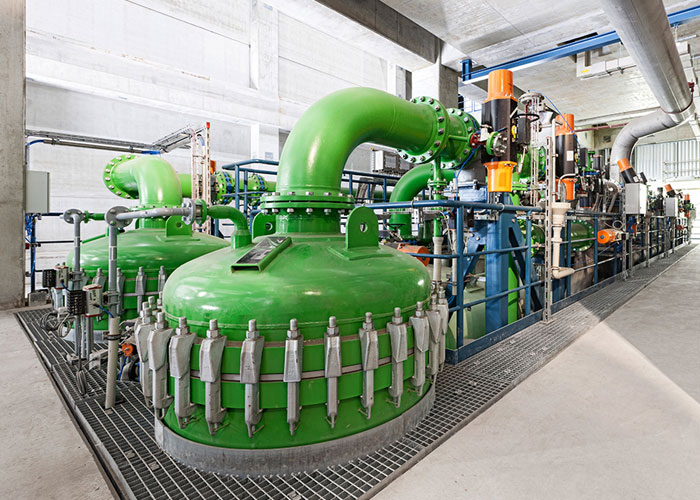

In today's industrial world, heavy metal pollution is a growing concern. Not only do these pollutants threaten the environment, but they also pose a health risk to humans. Fortunately, there are several ways to get rid of these pollutants. The most common methods involve adsorption on various materials and ion exchange on chelating ion exchangers.
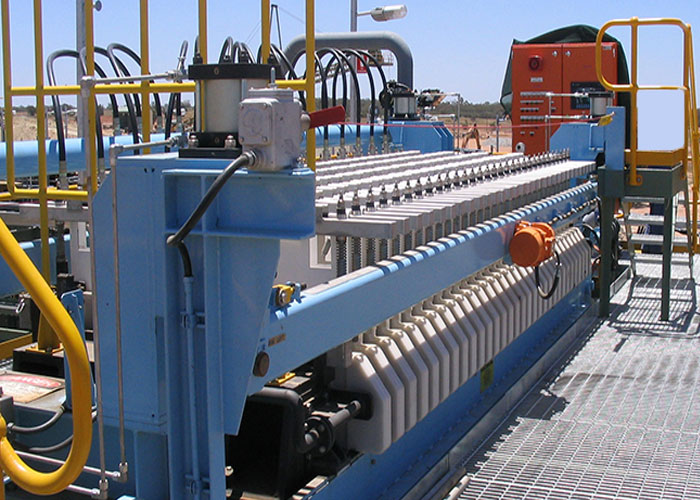
Chemical precipitation is an effective way to remove metal ions. Its low solubility allows it to achieve higher degrees of metal reduction in shorter periods of time. Additionally, this technique can be used over a wide pH range. And it's relatively inexpensive to implement.
Phytoremediation is another method used to remove heavy metals from wastewater. This technique utilizes plant species that can absorb these contaminants. This method is an important alternative to other methods because it is easy to implement and has several benefits. For instance, it can be used to remediate sites contaminated by industrial processes, such as power plants.
Impacts of EPA regulations on power plants
The Obama Administration's recent executive actions to curb emissions of greenhouse gases have posed challenges for power plants. The first rule, known as the "New Source Performance Standard," has made it nearly impossible to build a new coal-fired power plant. The second rule, the "Clean Power Plan," is intended to apply to existing power plants. This plan will require power plants to meet 47 different state standards and is projected to close down many power plants in the U.S.
The EPA plans to propose new rules to curb carbon emissions from power plants later this year. However, a Supreme Court ruling will likely prevent the agency from implementing its predecessor's Clean Power Plan, which would have reduced emissions by fuel-switching and trading. In the meantime, the agency will continue to evaluate its regulatory plans.
The Obama-era Clean Power Plan was a massive government effort to curb greenhouse gases. However, the Supreme Court blocked that rule in 2016 and ruled against the Trump administration's replacement rule. That means the EPA is scrambling to develop a rule that will survive judicial scrutiny. But, the government is running out of time to make meaningful climate policy changes.
Methods used to recover heavy metals
Several industrial processes generate sewage, which contains a variety of heavy metals. These include zinc, lead, mercury, cadmium, and chromium. Fortunately, there are methods for removing heavy metals from sewage to ensure that the wastewater does not cause health problems or environmental harm.
Chemical precipitation is a common method for removing heavy metals from wastewater. The process involves adding sulfides and hydroxides to the water to reduce the metal concentration. This method has the benefit of achieving a higher level of metal reduction in a shorter period. It is possible to apply this technique over a broad pH range.
The EPA's guidelines for power plant wastewater and coal combustion residuals force power plants to find solutions for removing heavy metals from wastewater. These regulations mandate that power plants limit the amount of process water they use in their FGD systems and have to develop systems to minimize the amount of this water in the final wastewater.







































Share Post